by G. Jack Urso
Hot Hero Sandwich had high production
values. It may have been a kids’ show, but NBC made available the same talent
behind the camera as it had on other shows filmed at 30 Rockefeller Center,
such as Saturday Night Live, with
which Hot Hero Sandwich is often
compared to, and indeed shared the same space at Studio 8H. Joel Spector, one of two audio
engineers for Hot Hero Sandwich, including
Scott Schachter (who has since passed away), exemplifies the kind of talent and
experience NBC nurtured at 30 Rockefeller Center.
By “nurture” I
don’t mean to infer they were being coddled. Rather, just the opposite. The
days, as Spector attests to, could run up to 22 hours long, multiple days a
week, for weeks on end. This would also entail working with demanding directors,
picky producers, and tight schedules, with millions of dollars on the line, so
only the absolute best in talent and temperament could be relied on in such an
environment and Joel Spector was one of those individuals.
 |
| Scott Schachter, left, and Joel Spector, right, circled in red and inset, at the Hot Hero Sandwich cast and crew group photo during the videotaping of Episode 10. |
Spector’s career
with NBC began in 1965, so he was already a 14-year veteran by the time Hot Hero Sandwich came along, prior to
which he was one of the audio engineers for Saturday
Night Live, which also included Scott Schachter. He served as chief audio engineer for The Macy’s Thanksgiving Day Parade for many years, as well as
working the board for David Letterman, the Tony Awards, and We Are One: The Obama Inaugural Celebration
at the Lincoln Memorial. Award shows, soap operas, talk shows, variety
shows, pre-recorded, or live when virtually anything and everything can happen,
Joel Spector’s steady hand in the audio control room ensured the sound was the
best.
Spector was the
audio engineer for the first two episodes, Scott Schachter
takes over for Spector beginning in episode 3, and they both join forces for episodes
10 and 11, whose boisterous on-stage finale, with an audience and full cast appearance, must have been a
challenge for the audio guys. For Hot
Hero Sandwich, a music-heavy program whose enduring memory is linked in
great part to its music performances, his importance to the show cannot be
understated.
In speaking with
Spector, however, it became clear there was also another crew member involved
with Hot Hero Sandwich I had been
neglecting — Studio 8H itself. Dating back to the 1930s, Studio 8H is like a
magnificent ship-of-the-line, retrofitted numerous times throughout its life to
keep pace with technology, it has been witness to history, and Joel Spector was
there.
And now he’s
here speaking with the Hot Hero Sandwich
Project, so let’s sit down and talk sound!
_______________________________________________________
Sounding
Off
Hot Hero Sandwich Project (HHSP): OK, to kick things off, one thing I have
heard repeatedly is how long the hours were during production. I imagine particularly
so for the crew who had to set up and tear down equipment.
Joel Spector: Oh, my God, the hours were
. . .
HHSP: “Insane,” I think is the word I heard
repeatedly. Was there a longest day that stands out all these years later?
Joel Spector: That was the last one, the absolute
longest was August 16, 6:00 AM to 4:30 AM. That was typical. I think
they didn't have a lot of time or maybe
they didn’t have a lot of availability for the cast or production.
HHSP: Yes, according to Ken Aymong [HHS
Production administrator], they had only about four weeks in total on Studio 8H.
Joel Spector: That's what it looks
like. July 12th was the first setup and the last day that I worked on it was
August 16th . . . Sister Sledge [episode 1], was recorded on the 17th of July.
We recorded three numbers, two of which were used — “We Are Family” and “He’s the
Greatest Dancer.” We also recorded “Lost the Music,” which we didn't use.
Sister Sledge performing “We Are Family” in
Episode 1 of Hot Hero Sandwich.
HHSP: I have to wonder where all that lost
footage ended up. They were all big hits!
Joel Spector: And somewhere along the line
there's the house band called Hot Hero.
HHSP: Yes! They’ve been very helpful to the project.
Joel Spector: Felix Pappalardi was in
charge of that . . . I see [referencing his notes] that it [the band] was on
camera in show one. I have notes about “record music” when it went on and an
audio recording at Mediasound which I attended in August. So, any other music
that I did was two-track far as I know. I know Scott Schachter did the other
shows, or most of the other shows, and I wasn't even around at that point — I
was on vacation — so, I don't know what he did.
[Note: Mediasound is the famous NYC
recording studio the Hot Hero Band laid down tracks at with Felix Papplardi and
Ed Stasium.]
The Hot Hero Band lays down the series’ theme
song in front of an audience during episode 2, for which Spector ran the sound.
HHSP: Well, we have the Scene-by-Scene rundowns for each episode, with links to each clip
for all those episodes, so we can track what went on for each episode you or
Scott did.
Joel Spector: I
just watch show one a little while ago— Bob Newman [Supervising Production Administrator] had a had a VHS video cassette
of it that he put on a disc for me, and it's not great, but I want to look at the
credits . . . it has his credits on, my credits are on, most of the credits are
on and then “clunk,” the recording stops because it's an air check.
HHSP: The credits cut out just before the
end on most of the copies I have — though I was lucky to even get the series.
It wasn’t until I got production documents from Hot Hero writer Marianne Meyer that I found a complete list of credits.
Commentary
Track
HHSP: Were you involved in recording sound
for segments beyond what was going on in Studio 8H?
Joel Spector: You know, this show has a
framework of interviews that are interspersed throughout . . .
HHSP: Yes. Dr. Tom Cottle was an early interview for the project.
Joel Spector: So, you know the whole story on that, and
that was on film, we [the studio crew] didn't do that. And it's very
interesting . . . I know one or two of the people that he interviewed and I
didn't know that she was being interviewed — Donna Pescow.
HHSP: Yes, Angie! [Pescow’s TV series].
Joel Spector: I think I've met her
once. She was very young. She's the daughter of someone who used to work with
my dad, who was a director.
HHSP: She talks about her dad. It was very revealing and as a child of
divorce, I could totally relate.
Joel Spector: There were a lot of
sketches. I would say the majority of what I did was on two booms.
HHSP: Really?
Joel Spector: There were what we call sketches, dramatic scenes . . . I see
that the music that we recorded was at one end of the studio, and the audience
was put around them. It wasn't anything to do with SNL [Saturday Night Live]. It was at the end of the studio that
doesn't normally have a stage, close to the control room, and that would be the
South end. That was designed by Leo (Akira) Yoshimura from Saturday Night Live. The non-musical portions of the shows were on sets all around the studio: the living room, cafe, classroom and some other sets.
HHSP: I know the music performances were
lip synced. I’ve always wondered about the tape source for those performances.
I’m guessing you didn’t use a cassette tape? Maybe 1/4 inch reel-to reel?
Joel Spector: The Sister Sledge segments were handled by first recording the band tracks on an 8-track 1-inch audio recorder. I then remixed those music tracks to mono on one of the spare tracks. We then played back that band mix to the stage monitor speakers and the studio PA speakers and the ladies sang live to those band tracks. Their vocals were recorded on individual tracks on the 8-track tape, along with SMPTE Time Code and "house sync". These same performances were simultaneously recorded on video tape with the same Time Code and sync signals, with each camera being recorded on a separate video tape. This facilitated the final video editing process.
Sister Sledge performing “He’s the Greatest
Dancer” in Episode 1 of Hot Hero Sandwich.
HHSP: How long did it take to record all
that?
Joel Spector: The Sister Sledge performances were remixed by me in 8H during the following week in two long sessions. I can't speak to any of the other episodes.
HHSP: Right.
Joel Spector: In "We Are Family" we did three complete takes of the song, and during the last take the Hot Hero cast and many young audience members come up to the stage to dance and sing with the sisters.[Note: Nan-Lynn
Nelson mentions that in her interview
with project.] That singing and dancing finale was cut probably in half. Then the kids
from the audience come up onto this, and that that's that got cut, probably in
half, very nicely by whoever edited that [Note:
Likely Hot Hero videotape editors
Harvey Berger and/or Bill Breshears], very nicely At the very end, one of the
sisters that I hear on the track, “Wooo!” [laughter]. They went full out. This
was in the morning. The ladies were ready and the band, it was their band and
they were smokin' hot!
HHSP: They were! There are a lot of great bands that played on Hot Hero, but
the energy of Sister Sledge is pretty hot. It was the perfect act to kick off
the series.
Inside
Studio 8H
The original configuration of Studio 8H, early
1930s.
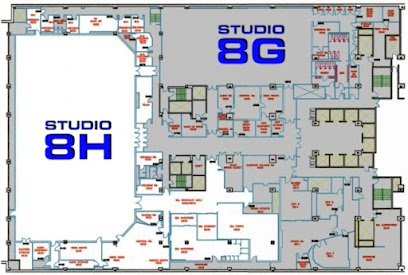 |
| The configuration of Studio 8H in 1979. Credit: SNL Senior Audio Engineer Robert Palladino and SNL Music Engineer Josiah Gluck. |
HHSP: I was reviewing the presentation you
participated in this past April for the Audio Engineering Society [AES, with
Robert Palladino, Senior Audio Engineer NABET at NBC Universal, and Josiah
Gluck, audio engineer on SNL], and I was fascinated by the history of Studio
8H going back to the 1930s when it was a radio broadcasting facility and radio
itself only about 40 years old at that point. The level of technology at the
point was already pretty complex. In the presentation you show an old photo of
a guy working on hundreds of cables at 30 Rock, and, as you note in the
presentation, there are no plug-and-play 50-pin connectors at the time, each
one of the wires has to be manually connected.
.bmp) |
| Einar Johnson, a technician wiring connections in master control at 30 Rock, circa 1930s (AES, April 2025). |
Joel Spector: That was in master
control, not the studio [8H]. The
studios had racks of equipment and at the bottom of each rack was a small
number of those “Christmas trees” . . . to get all the wires to and from all
the equipment at the mic outlets and then down to master control and the
associated equipment — they all use these connection blocks, terminal blocks, that's a tiny piece of what is the main distribution
frame, which is telephone company-type equipment . . . and that connects with
hundreds of racks in the equipment room and that enormous desk that you saw the
picture of in radio master control, and every studio has something like that. The
bottom of each rack was small like that. You've got to open the bottom of the rack
and go in there and wire things, so that stuff is tough, boy.
Master Control at 30 Rock, circa 1930s. It remained in service until the early 1960s (AES, April 2025).
HHSP: Another topic covered in the AES
presentation was how the floor plans to Studio 8H have changed over the years
to accommodate first radio, then TV, and then SNL. The floor plans were very helpful in trying to visualize where
the stages and control rooms were located in relation to each other. I guess
maybe in the circa 1976 setup, there's the control room and then there's a
sound room in between the control room and a video room.
Joel Spector: That's the audio room.
HHSP: The audio room rather. So, would that have been where you or were you
stationed?
Joel Spector: Yes.
 |
| The South end of Studio 8H where the Control Room, Audio Room (red arrow, above), and Video Booth were located circa the time of Hot Hero Sandwich, and close to the music performance stage. |
HHSP: Good. That helps put things in a
little bit more context. Here’s a little side story about the single
interaction I actually had with the control room at Studio 8H. I got a lot of
original production documents from one of the writers, Marianne Meyer, who was a great help to me at the start of the project, and in going
through them I found a call sheet and at the bottom is a phone number for
Studio 8H. Well, I figure after 45-50 years, that number had to be changed and
now it probably belongs to a pizza joint mid-town.
Joel Spector: I don’t think so . . .
HHSP: Oh, man, IT DID NOT! On the other end,
someone picks up and says, rather gruffly, “8H!” The number still went to the
control room! It was the middle of the day during a week SNL was on, so I panicked and hung up immediately! So, I am very
careful about what documents I post.
[laughter]
Joel Spector: The four digits [phone
number suffixes] don't tend to change.
HHSP: Well, my jaw dropped as soon as I
heard that!
Joel Spector: The thing from my end of
it [working at Studio 8H], we used the normal numbers . . . and it got to a point
where we finally got a real intercom. A real, big time intercom from McCurdy,
RTS McCurdy, and that ended up being alphanumeric. So, if you wanted to talk to
the 8H audio person you looked for 8H AU . . . certain people have their own four
character names, and so it just got to a point where people didn't remember the
numbers.
HHSP: Another aspect of the crew I’d like
to touch base on is that I understand that many of the crew who worked on SNL also worked on Hot Hero. In your
case, I see that’s true, and Leo [Akira] Yoshimura, the production designer who
worked on Hot Hero and SNL, and still does. Were there many
others?
Joel Spector: Hot Hero was done at the end of season 4 of SNL.
People worked on other projects that may have been in the studio. Looking at
it, I see I have 22 days in the studio. I did other things from time to time,
but some of these days, as I said — 6:00 AM to midnight, 6:00 AM to 3:00 — I
said to the music coordinator one day. “Well, look at this, the glamor of show
business, champagne and pizza at 3:00 AM.”
[laughter]
HHSP: Well, you gotta love the industry to
pull those hours! There were several sets used in each show. Did a lot of scene
changes contribute to the long days?
Joel Spector: As you've seen, watching
the shows, there are a lot of vignettes, a lot of scenes . . . Well, let's say that's about 44 scenes
that have to be taped in 30 days and I don't know how they jumped around. I
don't know if they did all the stuff in the living room . . . I don’t think so.
They probably had some standing sets and you did what you needed. There's a lot
of material to manage and, yet, I see that I worked on some other shows [during
that time], but, no, to answer your question directly.
HHSP: Right.
Joel Spector: When SNL is in
8H it's very difficult to fit almost anything else into the studio. They do 20
live shows a year and the audience bleachers have become a permanent part of
the studio. There are miles of wiring and racks of equipment built into them,
along with the Announce Booth. During the first five seasons that all was
removed once or twice for election night coverage, but eventually it became
“Sorry, that's the studio layout now.” Before SNL came in there, collapsible audience bleachers had been
installed along the North wall. You could have a game show and a soap opera set
up at the same time and go from one to the other, from one day to the next.
Those bleachers were eventually removed from the studio and were never used for
SNL.
HHSP: During the AES presentation, you
showed some images of 8H and when it was used in radio and for music performances
and it's just . . . WOW . . . it’s just enormous. Something it’s hard to
get a sense of by watching SNL, even
as I have all these years.
Joel Spector: Well, it's a block wide. It goes from
wall to wall 49th St. to 50th St. Essentially the playing area within that is
78 by 132 feet, and that's about the dimensions of the skating rink [the
famous ice skating rink at 30 Rock].
HHSP: That is huge!
Joel Spector: It is a big space, all column-free. There were many special broadcasts in that studio such as space shots, and on election nights it was filled with people, computers, tote boards, and “The Map” of the USA. That's why the SNL bleachers had to be removed. Election Night coverage now takes place outdoors in the skating rink, called “Democracy Plaza,” with huge graphics projected right onto the 30 Rock building.
On
Track
HHSP: A bit of a side question, but in the
AES presentation, you note at various points when 8H converted to a 24-track studio.
I think you mentioned this earlier on in our interview, if I recall correctly, that
you were using maybe just four or eight tracks in 1980?
Joel Spector: Yeah, and Hot Hero made the most use of that — and
which was only a couple days [laughter]. NBC had a Scully 1-inch 8-track recorder in the
Brooklyn Studios. They had renovated the Brooklyn 2 control room in the 70s for
Kraft Music Hall [an NBC variety
show] because they had a consultant from A&R Recording come in . . . and they determined that they wanted to have 8-track delivered to
post-production . . . and in 8H, we didn't use the multi-track for most things
because we did live shows.
HHSP: Right.
Joel Spector: Live from 8H, which was a Fred Silverman project at the end of the
70s. Three of the shows had live music, two with the New York Philharmonic, and one with the New American Orchestra from Los Angles, a salute to 100 Years of America's Popular Music with George Burns, the host. The fourth show was the New York City Ballet for which all the music was pre-recorded elsewhere.
HHSP: That would have been a complicated
show to manage.
Joel Spector: Scott Schachter [the
other Hot Hero audio engineer]
handled that.
HHSP: Thinking about the Sister Sledge
performances with the live audience, you allude in the AES presentation how
precise the microphones are. There’s still a lot of activity, people making
noise on stage, some of the crowd coming up on stage, and you can hear that
mixed in with the music. I think you mentioned in the AES presentation that you had
an audience boom you could use whenever you needed to, and it was pretty precise.
Was anything like that used?
Joel Spector: The boom was not involved
in the music production.
HHSP: No?
Joel Spector: Not at all. You have the Shure
SM58 for the vocals, those are close-talking microphones, and the ladies know
how to work those mics and we would work with the band and manage the playback
level and work with whoever our house engineer was, I guess he had the music
system on for that, I don’t know, but because it was a separate music system
for SNL. So, over the center of the
studio, big speakers — two big speakers, 4-way speakers, that can pump out a
lot of sound, but I don't remember any problems with that because we at that
point we knew what levels could be dealt with and the band was very cooperative.
HHSP: You still have that audience to deal
with.
Joel Spector: I've noticed listening
very carefully this morning, the crowd clapping and all that, that's live . . .
with other microphones and you just bring that in judiciously, and then any
cheers and applause during the episode, to me, that was posted [post-production]
somewhere else . . .
HHSP: In post [production] . . .
Joel Spector: That’s something that’s
very obviously not our stuff and put in somewhere else.
HHSP: You’ve seen a lot of changes in
technology during the course of your career.
Joel Spector: Boy, when we started
doing all these shows . . . I mean, I started doing this when I was 10 years
old, but with like, ¼-inch tape, by the time I did my last Tony Awards, which
was 2018 — music playback for 30 years on the Tonys and 33 years on the Macy’s
[Thanksgiving Day] Parade, things used to be all on tape, two guys with big tape
machines and big reels of tape, and all that. It ended up being me with two Lenovo laptops running SpotOn Playback, which is British
software made just to playback music and sound cues. The music department would upload to Dropbox the 100 cues for that show, which were recorded at an outside studio. So, finally, the production manager said
to me, “Write this name down . . . dedicated high-speed line.” Yes. “Write this
down . . . $10,000.”
[laughter]
HHSP: I can only imagine the size of those
data packages that would need that. You would need a dedicated high-speed line.
Joel Spector: Because the scenery was
electronic at that point, so that those guys with graphics and us, we needed it
. . . everything was in the computer, but, boy oh boy, you could turn on a dime
and so could the scenery. You could change the music cues, you could change a graphic cue, you could change all that stuff.
That's the
upside of that. The Tony’s and
Macy’s didn't abuse that flexibility. I know that with SNL, as we said at the AES presentation, from show #0001 to this
day, every time those words come out of an actor's mouth it’s the first time
that arrangement of words is heard. Because every time the scene is run it has been rewritten. That was not the case
with Hot Hero. You just rehearse it and do it, and maybe fuss with it just a
little bit, but that's it and “Next!” There was just too much to do.
HHSP: Yes, so much to do and so little time
to do it in.
Joel Spector: I tell you 18 hour days .
. . They [NBC] wanted to win Peabody
Awards. They hired Bruce and Carole Hart [Note: The Harts had previously won a Peabody
Award for Free to Be . . . You and Me.”]
HHSP: And they won Emmys.
Joel Spector: Yeah, they got Emmys, and I got a
nomination for that first show.
Rex Smith and the Hot Hero Band performing, “Tonight”
in episode 10.
HHSP: Yes, right, and Scott Schachter received
a nomination for episode 4. You and Scott were also on hand for episode 10 with
Rex Smith, who, I understand, according to writer Sherry Coben, showed up wearing a pair of the tightest pants on the planet . . . which showed a bit too much, so they had him change.
[laughter]
Joel, this
has been a great conversation, we’ve covered a lot of territory, and I think I’ve
taken up enough of your time today. You really set the record straight on what
was going on in Studio 8H and why things sounded so great. I’m very
appreciative of your time today. Thank you.
The boisterous finale in episode 11 with Andy Breckman, the Hot Hero Band, the cast, the audience, and the crew waves farewell. The last performance Joel Spector and Scott Schachter worked on for Hot Hero Sandwich.
_______________________________________________________
Concluding Thoughts
Joel Spector took us on a deep dive backstage at Studio 8H. Understanding the complexity and history of how things were done, gives us a better understanding of the craft and a greater appreciation of what Hot Hero Sandwich was able to accomplish in the relatively short time it had access to Studio 8H and its talented crew who ranked among the best in world at what they did.
Because of that, I have to admit,
I was a bit nervous speaking with Joel Spector and
felt like I was a 21-year-old broadcasting intern all over again. Though I fancy myself something
of an audiophile, I forgot the names of the expensive audio equipment, mics, and
software I owned. In fact, I forgot I even had a Shure SM58 mic, like those
used by Sister Sledge that Spector noted (and are still being made), and it is every bit as good as he reports.
As one will notice
throughout the interview, Spector kept meticulous records of what he was doing,
when he was doing it, and for how long he did it. In documenting the show’s
history, this information creates important anchor points for determining what
happened and when — something that becomes more challenging to piece together as
time goes by.
An oft-repeated
reprise of mine when it comes to Hot Hero
Sandwich is that despite there being no VHS, CDs, DVDs, or even an album released, the show’s fans still remembered the music, sketches, and animation. An
amazing achievement not just of the creators, but also of those tasked
with bringing their vision to the screen and Joel Spector, along with Scott Schachter, gave that vision a voice.
And it's one we're still listening to 45 years later.
Special thanks to Ken Aymong, production administrator for Hot Hero Sandwich, for introducing me
to Joel. Thanks Ken!
___________________________________________________
Audio Engineering vs. Sound Engineering
To clarify, there
is a difference between the audio engineering Joel Spector did and the sound engineering
Ed Stasium did for Felix Pappalardi for the series (which Stasium discusses in his interview
with Hot Hero Sandwich Project). Spector’s
work has been with live and pre-recorded televised performances, usually
working with a full stage and technical crew, while Stasium’s career was primarily
in recording studios, working closely with artists and their instruments to best
capture their “sound.” The studios Stasium recorded in would be far smaller
than ones like Studio 8H, where Spector plied his trade, and often included an
audience, which the studios Stasium worked in did not.
● ● ●





.bmp)






No comments:
Post a Comment